Enterprise Web App Development Guide
Our expert guide to enterprise web app development covers strategy, architecture, and technology to help you build scalable and secure solutions.Enterprise web app development isn't just about building software; it's the strategic blueprint for creating large-scale, custom solutions that tackle a company's biggest operational headaches.
Think of it this way: if a standard consumer app is a house, an enterprise app is the entire city's infrastructure. It's engineered from the ground up to be the digital backbone for a business's most critical, high-stakes operations.
What Enterprise Web App Development Really Means
At its heart, enterprise web development goes way beyond simple functions and a slick user interface. It’s about building a powerful, centralized system that weaves itself into the very fabric of an organization's operations. These aren't just standalone tools. They're complex ecosystems designed to support thousands of users, process massive volumes of sensitive data, and automate workflows that the business absolutely depends on.
This is a world away from creating a typical app. A consumer-facing app might be laser-focused on a single, streamlined user journey, but an enterprise application has to juggle hundreds of intricate business processes all at once. That's why the whole process feels more like architectural engineering than traditional software coding. To see how this compares with mobile-first projects, you can explore the approach a specialized mobile app development company takes.
To better illustrate the difference, let's break down the key distinctions.
Standard vs Enterprise Web Apps At a Glance
This table highlights the fundamental distinctions in scope, complexity, and requirements for enterprise applications compared to standard consumer-facing web apps.
| Characteristic | Standard Web App | Enterprise Web App |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | User engagement, conversions | Business process automation, efficiency |
| User Base | General public (consumers) | Internal employees, partners, B2B clients |
| Scale & Complexity | Simple, focused functionality | Complex, multi-faceted workflows |
| Data Sensitivity | Low to moderate (e.g., user profiles) | High (e.g., financial, patient, proprietary data) |
| Integration Needs | Minimal (social logins, payment gateways) | Extensive (ERPs, CRMs, legacy systems) |
| Security | Important, but standard measures often suffice | Mission-critical, requiring multi-layered defenses and compliance |
As you can see, the stakes are simply higher with enterprise systems. Every decision, from architecture to security protocols, carries more weight.
The Defining Characteristics
So, what truly elevates an application to "enterprise-grade"? It really comes down to a few non-negotiable pillars that set these systems apart from their smaller-scale cousins. These aren't just extra features; they're foundational principles baked into the application's DNA from day one.
Here are the core attributes you'll always find:
Massive Scalability: The system has to perform flawlessly whether it's supporting 100 users or 100,000, often scattered across different continents and time zones. A practical example is a global logistics company's app—it must manage thousands of simultaneous shipment trackings and inventory updates during peak holiday season without a single hiccup.
Robust Security: We're talking about systems that handle the crown jewels: financial records, private employee information, and sensitive business intelligence. Security isn't just a feature; it's a multi-layered fortress built to meet strict compliance standards like GDPR or HIPAA. For a healthcare provider, this means implementing end-to-end encryption for all patient data, both in transit and at rest.
Seamless Integration: An enterprise application can't live on an island. It has to communicate perfectly with dozens of other systems. For instance, a new sales CRM must pull customer data from a 20-year-old legacy database, push order details to the SAP ERP system, and sync with a third-party marketing automation tool like Marketo.
Ultimately, enterprise web app development is about building a durable, long-term asset that drives efficiency and growth. It's the digital engine that powers the business, enabling it to operate at scale while remaining agile and secure. This foundation is essential for any organization looking to achieve lasting operational excellence.
The Three Pillars of Enterprise Web Apps
When you're building an enterprise web application, you're not just building software. You're building a foundational piece of a business's operations. Get it wrong, and you can cause operational chaos, financial loss, and serious security breaches. Get it right, and you create a powerful engine for growth.
Everything comes down to three core pillars. These aren't just buzzwords or nice-to-have features; they are the absolute, non-negotiable principles that determine whether an enterprise app will stand or fall.
Think of them like the legs of a tripod. If one is weak or missing, the whole thing becomes unstable and is guaranteed to topple under pressure. Let's break down what each one means in the real world.
1. Scalability and Performance: The Electrical Grid
Imagine your application is the electrical grid for a major city. On a normal day, it hums along, delivering consistent power to everyone. But what happens during a massive heatwave when every single air conditioner kicks on at once? The grid has to handle that peak demand without browning out.
That’s the essence of scalability and performance. Your app has to perform just as flawlessly for 500 employees on a quiet Monday morning as it does for 50,000 global users during a Black Friday sale. If it can't scale, the system will slow to a crawl, crash, and bring business to a screeching halt when you need it most.
For example, a major e-commerce platform that fails to scale during the holiday rush doesn't just lose a few hours of sales. It suffers a blow to its brand reputation, loses customer trust, and directly sends shoppers to competitors. The financial and brand damage can take months to repair.
A truly scalable application is designed for growth from day one. It anticipates future demand and is built to expand its capacity without a hitch, ensuring a smooth user experience no matter the load.
Achieving this level of reliability involves a few key strategies:
- Load Balancing: This distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers, so no single one gets overwhelmed. For example, a ticketing website uses a load balancer to handle the massive surge of users the moment concert tickets go on sale.
- Cloud Infrastructure: Using services like AWS or Azure allows for "elastic scaling," where the system automatically adds more server capacity during traffic spikes and scales back down when things quiet down, optimizing costs.
- Efficient Database Design: A well-organized database can find and retrieve information in milliseconds. An actionable tip is to index frequently queried columns in your database, which dramatically speeds up search operations. It's also smart to run a UX design audit, which can uncover performance bottlenecks from the user's point of view, making sure the front-end feels just as fast as the back-end is.
2. Security and Compliance: The Digital Fortress
In the enterprise world, security isn't just a lock on the front door; it’s a multi-layered digital fortress. This pillar is all about guarding a company's crown jewels: its data, its intellectual property, and its customer information. The threats are constant and evolving.
A security breach in an enterprise system is nothing short of catastrophic. Picture a healthcare app leaking patient records. The fallout is immediate and severe: massive fines under regulations like HIPAA, class-action lawsuits, and a complete erosion of public trust.
Modern enterprise security is a complex, ever-moving target. As a guide on web application development from BrowserStack points out, security remains a top concern for businesses facing a constant barrage of global cyber threats. It’s not enough to just react; you have to be proactive. This also means strict adherence to data privacy laws like GDPR, which mandate robust data encryption and clear policies on how user data is handled.
A comprehensive security model includes:
- Data Encryption: This scrambles data so it's unreadable to unauthorized parties. A practical step is to enforce TLS 1.2 or higher for all data in transit and use AES-256 encryption for data at rest in the database.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): This is the principle of least privilege. For example, a sales representative should be able to view their own customer accounts but be blocked from accessing the finance department's payroll data.
- Regular Security Audits: This means proactively hiring third-party firms to conduct penetration testing and running automated vulnerability scans on your codebase after every major update to find weaknesses before attackers do.
3. Integration and Interoperability: The Universal Translator
No enterprise app is an island. It has to connect and communicate with a whole ecosystem of other software—from creaky old legacy systems to modern cloud services and third-party APIs. This is integration and interoperability.
Think of it as the universal translator for your entire company. Your CRM needs to talk to your marketing platform, which has to sync with your ERP, which then feeds data into your financial reporting tools. Without these seamless connections, you end up with data silos, broken workflows, and people stuck doing tedious, error-prone manual data entry.
Here’s a practical example: a manufacturing company rolls out a new inventory management app, but it can't communicate with their decades-old accounting software. The result? The finance team spends hours manually re-entering sales data into the old system, leading to costly invoicing errors and no real-time view of the company's financial health. Strong enterprise web app development prevents this by building robust APIs that ensure every system speaks the same language from day one.
Choosing the Right Architectural Blueprint
Picking an architecture for your enterprise web app is a lot like choosing the blueprint for a skyscraper. It’s a decision you make long before a single line of code gets written, yet it dictates the strength, flexibility, and future of the entire structure. The right blueprint lets your application grow and adapt; the wrong one can lead to costly renovations or, worse, a complete tear-down.
This isn't just some techy detail. It's a strategic business decision that directly impacts how fast you can develop, what your maintenance costs look like, and whether you can handle growth. Let’s break down the three most common architectural patterns using some real-world analogies to make sense of them.
This diagram shows how the different layers of a typical web app fit together—from what the user sees on their screen to the back-end logic and the database that holds all the data.
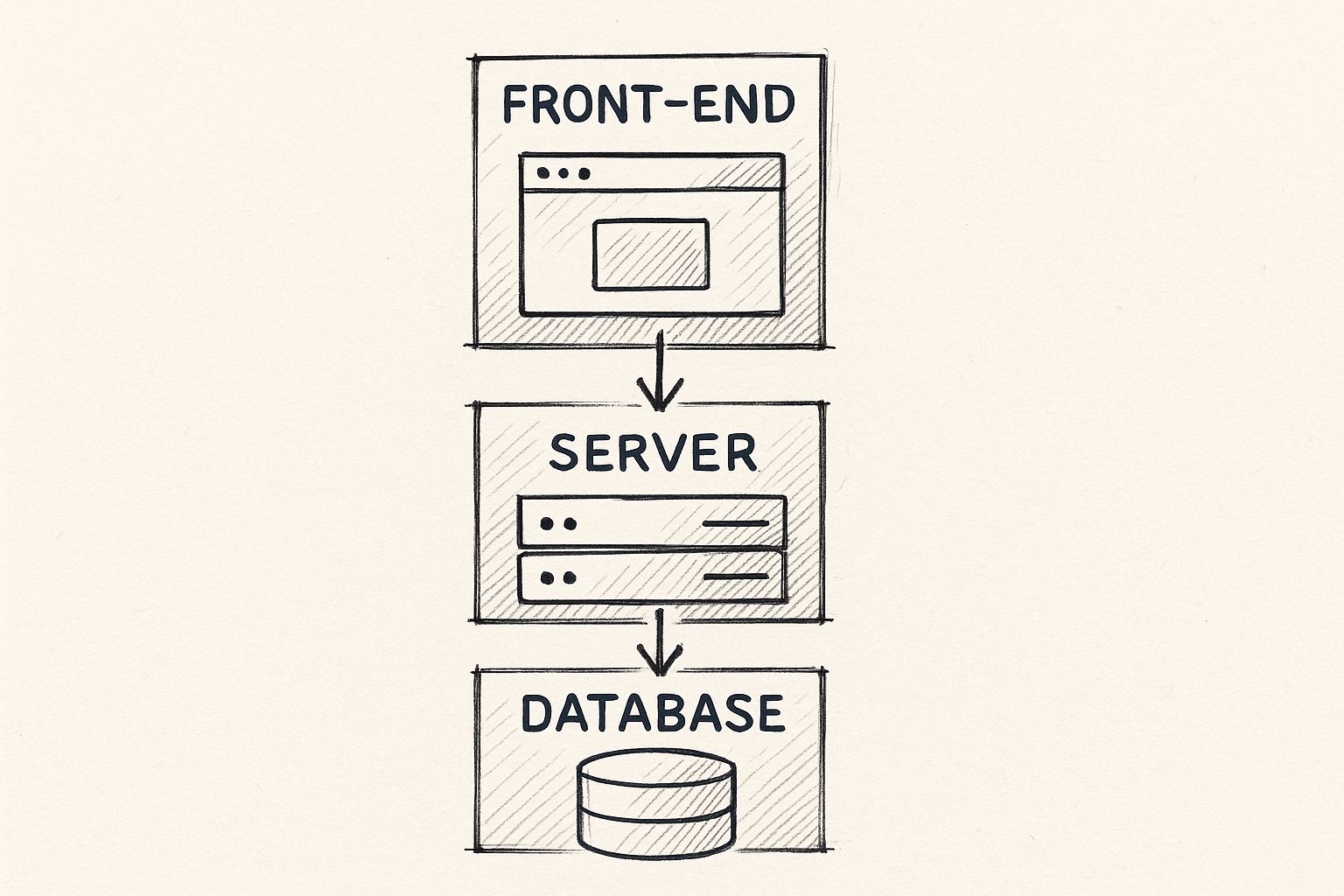
The big takeaway here is that everything is connected. The architecture you choose defines exactly how these layers talk to each other and how the whole system scales.
Monolithic Architecture: The All-in-One Superstore
Think of a monolithic architecture as a massive, all-in-one superstore. Everything you could possibly need—the user interface, all the business logic, and the database connections—is housed under a single, massive roof. The entire application is built as one unified piece.
This approach is wonderfully straightforward. It’s often faster to get started with because all the components are tightly coupled, making communication between them direct and simple. For smaller projects or startups just trying to get a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) out the door, this simplicity is a huge plus.
But the "superstore" model has its downsides. Imagine trying to renovate just the bakery section. You'd probably have to disrupt the entire store to do it. It's the same with a monolith. If you want to update one tiny feature, you have to redeploy the entire application. That’s risky and slow. Scaling is also an all-or-nothing game; if one part of your app gets a surge in traffic, you have to scale the whole thing, which is far from efficient.
Microservices Architecture: The Modern Shopping Mall
Now, picture a modern shopping mall. Instead of one giant store, you have dozens of independent, specialized boutiques. Each boutique is a microservice that handles a specific job—one for payment processing, another for user accounts, and a third for managing product inventory.
Each of these services is developed, deployed, and scaled on its own. This is the superpower of the microservices approach. If the payment "boutique" needs an upgrade, you can work on it without touching the inventory or user account services. For a company like Netflix, this means they can update their recommendation algorithm (one service) without affecting the video streaming service or user authentication service.
Microservices offer incredible flexibility and scalability, which is why they've become so popular for complex enterprise apps. In fact, one report shows that 63% of enterprises have already adopted microservices to ship software faster and make their systems more resilient.
Of course, managing a mall is way more complicated than running a single store. You need a good management system (things like an API gateway and service discovery tools) to make sure all the independent boutiques work together smoothly. The communication between all these services can also add a bit of lag if you're not careful.
Serverless Architecture: The Pop-Up Shop
Finally, let's look at serverless architecture. This is like leasing a fully-staffed pop-up shop that only opens for business when customers actually show up. With this model, you don't manage any servers at all. Zero. Instead, you write your application logic as a collection of functions, and a cloud provider (like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions) handles everything else—setting up, managing, and scaling the infrastructure needed to run them.
You only pay for the exact time your functions are running, right down to the millisecond. This can be unbelievably cost-effective, especially for applications with unpredictable or spiky traffic. A practical example is an image processing function for a social media app. It only runs for a few seconds when a user uploads a photo and costs nothing the rest of the time.
The trade-off? You give up a lot of control. You're living in the cloud provider's world, which can lead to vendor lock-in. Debugging can also be a headache, as you’re trying to trace a problem across a distributed, event-driven system that you don't fully own.
Making the Right Choice
So, which blueprint is right for you? It completely depends on what you're building. There's no single "best" answer.
- Choose Monolithic if: You have a small team, a fairly simple application, and your main goal is to launch quickly. A great example is an internal HR portal for a mid-sized company.
- Choose Microservices if: You're building a large, complex system like a banking platform or a global e-commerce site, have multiple development teams, and need serious scalability and long-term flexibility.
- Choose Serverless if: Your app relies on event-driven tasks (like sending a confirmation email after a purchase) or has unpredictable traffic, and you want to slash infrastructure overhead and costs.
For organizations trying to weigh these options, getting an expert opinion can make all the difference. Looking into services like outsourcing product development can connect you with seasoned architects who have navigated these exact decisions on dozens of successful projects, ensuring your foundation is built to last.
Assembling Your Modern Technology Stack
Choosing the right technology stack is a lot like a master chef picking their knives. Every tool has a purpose, and the combination you end up with directly impacts the quality, speed, and even the "flavor" of the final product. For an enterprise web application, this isn't just a technical choice; it's a foundational business decision that shapes everything from performance and scalability to your hiring pool and long-term maintenance costs.
Making a smart call here means striking a balance—weighing the raw technical power of each component against your business goals and the real-world talent you can bring on board.
Crafting the User-Facing Experience
The front-end is everything your users see and touch. It’s the application's face. Think of it like a car's dashboard. Some are built for expert drivers who want total control and customization, while others offer a more guided, all-inclusive experience that’s simpler to manage.
React: I like to think of React as a box of high-performance, interchangeable LEGO bricks. It gives developers incredible freedom to build a completely custom user interface from the ground up. This makes it perfect for dynamic, interactive apps like a real-time stock trading dashboard where charts and figures must update instantly.
Angular: On the other hand, Angular is more like a luxury car's fully integrated dashboard system. It arrives as a complete, opinionated package with everything you need—from routing and state management to form validation—already built-in. This structure enforces consistency, which is a huge advantage for a large bank building a suite of internal applications that must all have the same look, feel, and security standards.
Ultimately, the decision often hinges on your team's background and the project's demands. If you're building a prototype and need to move fast, React's flexibility is a huge plus. But for a massive enterprise system that needs to be stable and maintainable for years, Angular’s rigid structure can be a lifesaver.
Powering the Back-End Engine
If the front-end is the dashboard, the back-end is the engine room. This is where all the real work gets done: processing data, executing business rules, and talking to other systems. The language you pick here dictates how well that engine performs under pressure.
Java & .NET: These are the heavy-duty, industrial-strength workhorses of the enterprise world. Famous for their security, stability, and massive ecosystems, they are purpose-built for creating complex, data-heavy applications. You'd use these to power a global financial trading platform or a sprawling ERP system for a Fortune 500 company.
Node.js: In contrast, Node.js is the lightweight, high-revving engine designed for raw speed and real-time communication. Its non-blocking architecture is a game-changer for apps that need to juggle thousands of simultaneous connections, like a customer support live chat platform or a collaborative project management tool like Trello.
For a closer look at how these pieces fit together, exploring real-world examples of custom web application development can shed light on how to build a powerful, cohesive system.
Choosing Your Data Storage System
Every enterprise app needs a place to store its information, and this brings us to the database. The two main philosophies are SQL and NoSQL. The best way I've found to explain the difference is with a simple analogy.
A SQL database is like a meticulously organized library. Every book (your data) has a designated spot on a specific shelf (a table) and a detailed card catalog entry (the schema) that defines its structure and location. This makes finding related pieces of information incredibly fast and reliable.
A NoSQL database, by contrast, is more like a modern, searchable digital archive. You can toss in all kinds of documents and files without worrying about a predefined structure, making it incredibly flexible for handling huge volumes of varied, unstructured data.
This screenshot from StackShare.io shows how major companies like Uber and Airbnb build their tech stacks. It’s a great illustration of how different tools are combined to solve different problems.
Notice that neither company sticks to just one technology. They mix and match, picking the best tool for each specific job.
Here’s a quick cheat sheet for when to use each:
- Go with SQL (e.g., PostgreSQL, MySQL): When data integrity is non-negotiable, like in a banking application where every transaction must be perfectly recorded and accounted for.
- Go with NoSQL (e.g., MongoDB, Cassandra): When you need to scale to handle massive amounts of unstructured data, like a social media platform storing billions of user posts, comments, and images.
Putting together a solid, future-proof tech stack is about more than just chasing the latest trends. It’s about creating a synergistic system where every component strengthens the others, all while aligning perfectly with your business goals and empowering your team to do their best work.
How AI and Low-Code Are Changing the Game
If you look at the world of enterprise web app development right now, you’ll see two massive shifts happening simultaneously. First, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are moving from the R&D lab to the core of business operations. At the same time, low-code platforms are completely changing who can build software and how fast they can get it done.

This isn't just about bolting on a few flashy new features. We're talking about a fundamental change in how companies solve problems, innovate, and compete. Getting a handle on these trends is quickly becoming non-negotiable for any business that wants to stay relevant.
AI and Machine Learning: The New Brains of the Operation
AI isn't science fiction anymore; it’s a practical engine for real-world business results. The enterprise application software market is expected to hit a staggering $569 billion by 2027, and a huge part of that growth comes from embedding AI and ML to make workforces smarter and operations smoother. You can dig deeper into these enterprise application development trends to see just how big the impact is.
The best way to think about AI is as an intelligence layer that sits over your existing business systems. It’s constantly scanning for patterns and making predictions that a human team, no matter how skilled, could never spot. It transforms a standard enterprise app from a simple database into an active partner that helps you make better decisions.
Take a global logistics company, for example. They were constantly battling unpredictable shipping delays. By integrating an AI model into their supply chain app, they can now analyze thousands of variables in real time—weather, port congestion, traffic jams, you name it—to see disruptions coming before they happen.
The app doesn't just send an alert. It proactively suggests and even executes the best alternate routes to keep deliveries on schedule. That one AI-powered feature can save millions in costs and prevent a whole lot of angry customer phone calls.
Here are some other practical examples:
- Predictive Maintenance: A factory integrates AI that analyzes data from machinery sensors. The system predicts a specific bearing will fail in the next 72 hours, allowing the team to schedule maintenance proactively and avoid a catastrophic shutdown.
- Personalized Customer Experiences: An e-commerce site uses ML to analyze a user's browsing history and purchase patterns, then serves up product recommendations so accurate they feel hand-picked, significantly boosting conversion rates.
- Fraud Detection: A financial services app uses AI to monitor transactions in real time. It instantly flags and freezes a suspicious transaction that deviates from a user's normal spending habits, preventing fraud before it happens.
The Rise of Low-Code and the "Citizen Developer"
So, if AI provides the brains, low-code and no-code platforms are all about democratizing the building process. These tools offer visual, drag-and-drop interfaces that drastically cut down on the need for traditional, line-by-line coding.
It's like giving your business teams a high-end LEGO set instead of a pile of raw materials. This empowers employees who aren't trained developers—often called "citizen developers"—to build simple apps and automate their own departmental tasks. For example, an HR manager could use a low-code platform to build a simple vacation request and approval app in an afternoon, without writing any code.
This is a huge relief for the central IT department. Instead of being swamped with a never-ending backlog of requests for small tools and custom reports, the professional developers can focus their energy on the big, complex, mission-critical enterprise web app development projects that truly require their expertise.
Putting It All Together for a Competitive Edge
Jumping into these technologies doesn’t mean you have to rip and replace everything you've already built. The smart approach is strategic and incremental.
Here’s a practical, actionable plan to get started:
- Find the High-Impact Spots: Start by identifying a business process that is repetitive, data-heavy, or prone to human error. A great first project could be automating the sales lead assignment process.
- Empower with Low-Code: Provide a low-code tool (like Microsoft Power Apps or Retool) to a tech-savvy team in HR or Marketing. Task them with building a simple internal tool, such as an app for tracking marketing campaign spend.
- Set Up Guardrails: Create a "Center of Excellence." This team establishes clear governance rules, defines what citizen developers are allowed to build, controls data access, and provides training to ensure security and prevent a chaotic free-for-all of "shadow IT."
By thoughtfully blending the predictive power of AI with the speed and accessibility of low-code platforms, you create a culture where everyone is empowered to improve their own workflows. The result is a more agile, responsive, and innovative organization.
Your Enterprise Development Questions, Answered
Jumping into an enterprise web app project can feel daunting. The stakes are high, the investment is significant, and you've undoubtedly got questions about what to expect. Getting straight answers is the first step toward making smart decisions and launching a successful product.
Let's cut through the noise and tackle some of the most common questions we hear from business leaders and technical teams.
How Long Does Enterprise Web App Development Take?
There's no magic number here. The timeline for an enterprise app depends entirely on its complexity, how many other systems it needs to talk to, the architecture we choose, and the size of the team building it. For instance, a project using a microservices architecture might take longer to set up initially compared to a more traditional, monolithic application.
As a rule of thumb, a typical enterprise project can take anywhere from 6 to 12+ months. A smarter way to approach it, though, is with a phased rollout. We almost always recommend starting with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP).
An MVP is all about getting the absolute core features into the hands of real users as quickly as possible. For a new inventory management system, the MVP might only include the ability to scan barcodes and update stock counts, leaving reporting and forecasting for a later phase. This approach lets you launch a functional first version in as little as 4-6 months.
What Is the Biggest Mistake to Avoid?
This one is easy: skimping on the discovery and planning phase. It's the single most common and costly mistake we see. Everyone feels the pressure to start coding, but treating this foundational stage as an optional step is a surefire way to invite disaster.
When you rush into development without a crystal-clear, shared understanding of user needs, business logic, and technical requirements, you end up with rework, blown budgets, and a product that misses the mark. For example, building an entire module based on a misunderstood requirement can waste hundreds of development hours.
Think of a thorough discovery phase as both the blueprint and the insurance policy for your project. A practical action is to insist on creating detailed user stories and wireframes that stakeholders must sign off on before any code is written.
How Do You Ensure an Application Can Scale?
Scalability isn't something you can add on later. It has to be baked into the application's DNA from the very first line of code. An app that works beautifully for 100 users needs to be built to handle 100,000 without breaking a sweat. If you don't plan for growth, you're just building future bottlenecks that will grind your operations to a halt.
So, how do we build for scale? It comes down to a few key strategies:
- Pick a Scalable Architecture: Modern patterns like microservices or serverless architecture give you the power to scale individual parts of the app independently as needed.
- Embrace Cloud Infrastructure: Platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are designed for this. They allow for "elastic scaling," automatically adding or removing resources based on live traffic.
- Implement Load Balancing: This is like a traffic cop for your app. It intelligently distributes incoming requests across multiple servers so no single one gets overwhelmed during peak hours.
- Design a Resilient Database: Your database is often the first thing to buckle under pressure. An actionable strategy is to use read replicas, where copies of your database handle read requests, freeing up the primary database to focus on writes.
Will Low-Code Platforms Replace Developers?
The rise of low-code and no-code tools is definitely changing the game. This isn't just a small trend—it's exploding. By 2025, Gartner predicts that 70% of new enterprise applications will be built on these platforms, a massive leap from under 25% in 2020. This shift is happening because it promises faster delivery and lower costs. You can read more about the growth of the no-code market on Adalo.com.
But this doesn't mean professional developers are going anywhere. Instead, their roles are evolving.
Low-code platforms are fantastic for empowering "citizen developers"—think of a tech-savvy marketing manager or a process-oriented operations lead. They can now build simple departmental apps or automate workflows without waiting in line for the IT department. This is a huge win, as it frees up professional developers from a backlog of smaller tasks.
This allows seasoned developers to focus on what they do best: engineering the complex, high-stakes, mission-critical systems that run the business. They become the architects of the secure, scalable foundations that low-code tools simply can't build. When the project is truly complex, expert digital product development services are still the key to getting it right.
At Pixel One, we specialize in transforming complex business challenges into simple, scalable digital products. From strategy and design to full-stack development, we guide you through every stage to ensure your enterprise web app delivers measurable impact. Talk to our experts today and let's build the future of your business together.